Flash Point
Little Pro on 2016-01-13
Flash point is the lowest temperature at which a chemical can vaporize to form an ignitable mixture in air. A lower flash point indicates higher flammability. Measuring a flash point (open-cup or close-cup) requires an ignition source. At the flash point, the vapor may cease to burn when the ignition source is removed. You can often find it in the section 9 of a safety data sheet (SDS).
It shall be note that flash point is different from auto-ignition temperature at which a chemical can burn without an ignition source.
Regulatory Implications of Flash Point
Flash point is mainly used to distinguish flammable liquids from combustible liquids and non-flammable liquids. The picture below is an example of GHS classification criteria for flammable liquids. A liquid with a flash point between 23 and 60 Celsius degrees will be classified as flammable liquid category 3. A liquid with a flash point above 93 Celsius degrees does not meet GHS classification criteria and will not be regarded as a flammable liquid or a hazardous chemical.
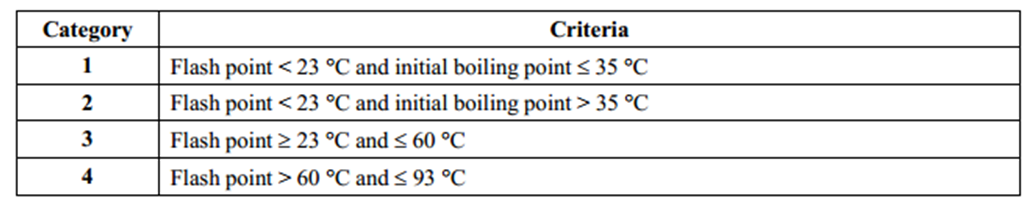
Under dangerous goods regulations, a liquid with a flash point below 60 Celsius degrees will be classified as Class 3 Dangerous Goods FLAMMABLE LIQUIDS. Materials with flash points below 100 °F (38 °C) are regulated in the United States by OSHA as potential workplace hazards.
Under REACH, a flash point test does not need to be conducted if:
- a chemical is inorganic, or
- a chemical only contains volatile organic components with flash-points above 100 °C for aqueous solutions, or
- the estimated flash-point is above 200 °C, or
- the flash-point can be accurately predicted by interpolation from existing characterised materials.
More Physicochemical Properties and Their Regulatory Implications
- Physical State, Appearance & Odour;
- Melting point;
- Boiling Point;
- Relative Density;
- Flash Point;
- Vapor Pressure;
- Henry's Law Constant;
- Surface Tension;
- Water Solubility;
- n-Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient;
- pH;
- Flammability;
- Oxidising Properties;
- Explosive Properties;
- Granulometry;
- Explosive Limits;
- Viscosity;
- Dissociation Constant;
Having Questions?
We do not provide consultancy services. If you have questions or need any help, please contact our sponsor. You may also find an expert in CSP business directory below. If you are a consultant, you may get yourself listed in CSP business directory (free) or sponsor this page to leave your contact info on this page..

Tags: Topics - CRA, Physiochemical Property