GHS Hazard Class and Hazard Category
Little Pro on 2016-01-06
GHS describes the nature and severity of a chemical hazard by hazard class and hazard category:
- GHS hazard class represents the nature of a chemical hazard, i.e., flammable liquids, carcinogen.
- GHS hazard category is the division of criteria within each hazard class. For example, hazard class flammable liquids can be divided into 4 categories among which flammable liquids category 1 represents the most severe hazard.
There are 29 GHS hazard classes in total in UN GHS Rev. 6. They are used to describe 3 main types of chemical hazards: physical hazards, health hazards and environmental hazards. If you wish to find hazard statements and signal word for each hazard category, please use our hazard statement and signal word finder.
| Physical Hazards(17 classes) |
|
| Health Hazards(10 classes) |
|
| Environmental Hazards(2 classes) |
|
Determination of GHS Hazard Class and Hazard Category
GHS has provided standard chemical classification criteria which are used to determine the hazard class and hazard category of a chemical. The picture below is an example of GHS classification criteria for flammable liquids. A liquid with a flash point between 23 and 60 Celsius degrees will be classified as flammable liquid category 3. A liquid with a flash point above 93 Celsius degrees does not meet GHS classification criteria and will not be regarded as a hazardous chemical.
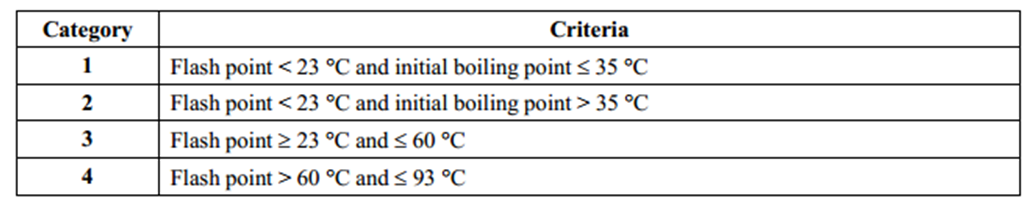
Download GHS Classification Criteria
- The latest summary of GHS classification criteria in a single page;
- UN Purple Book: Classification criteria for physical hazards;
- UN Purple Book: Classification criteria for health hazards;
- UN Purple Book:Classification criteria for environmental hazards.
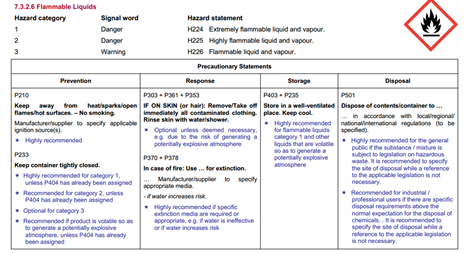
Standard hazard pictograms, hazard statements and precautionary statements will be assigned once the hazard class and hazard category of a chemical has been determined. (see example below).
Adoption of GHS Hazard Class & Hazard Category in Individual Countries.
GHS allows individual countries or regions to choose which hazard classes or hazard categories to implement to meet their domestic needs. For example, EU has not adopted flammable liquids category 4. The United States has not adopted Hazardous to the Ozone Layer yet. This is often called GHS Building Block approach.
Reference & Resources
Advanced GHS Readings
- Global GHS Label Size Requirement
- Global GHS Label Requirement for Small Containers
- GHS and Pesticides
- GHS Classification List
- GHS and Confidential Business Info
- List of GHS Resources and Regulations
- Comparing GHS Builing Blocks in EU, USA, China and Japan
- Correlations between TDG and GHS
- When Should You Update Your SDSs
Having Questions?
We do not provide consultancy services. If you have questions or need any help, please contact our sponsor. You may also find an expert in CSP business directory below. If you are a consultant, you may get yourself listed in CSP business directory (free) or sponsor this page to leave your contact info on this page..

Tags: Topics - GHS, GHS Basics and Tutorials