How to Calculate Predicted No-Effect Concentration (PNEC)
Little Pro on 2016-07-13
Predicted No-Effect Concentration (PNEC) is the concentration of a substance in any environment below which adverse effects will most likely not occur during long term or short term exposure. In environmental risk assessment, PNECs will be compared to actual or predicted environmental concentration (PEC) to determine if the risk of a substance is acceptable or not. If PEC/PNECs<1, the risk is acceptable.
Predicted No-Effect Concentration (PNEC) Example - Acetone
According to this source, the PNEC-fresh water of acetone is 10.6mg/L. That means that if the concentration of acetone present in fresh water (pond/lake/river) is below than 10.6mg/L, the acetone will unlikely cause adverse effects to the aquatic environment. This value is not set randomly. There is a systematic and scientific way to derive it. Please continue reading.
How to Derive Predicted No-Effect Concentration (PNEC)?
The PNECs are usually calculated by dividing toxicological dose descriptors by an assessment factor. The endpoints most frequently used for deriving PNECs are mortality (LC50), growth (ECx or NOEC) and reproduction (ECx or NOEC).
- LC50 /EC50 (Median Lethal Concentration/Median Effective Concentration): They are the concentrations at which 50% mortality or inhibition of a function (e.g. growth or growth rate) was observed. They are usually obtained from short-term eco-toxicology studies.
- NOEC (No Observed Effect Concentration): NOEC is the highest tested concentration for which there are no statistical significant difference of effect when compared to the control group. It is usually obtained from long-term eco-toxicology studies. In some studies, only LOEC (lowest observed effect concentration) can be obtained, in which case NOEC can be calculated as LOEC/2.
- ECx: It is the concentrations at which x % (10% for EC10) effect was observed or derived statistically when compared to the control group. It is usually obtained from long-term eco-toxicity studies.
- Typical units: mg/L or mg/kg.
The table below is an example of how to calculate Derive Predicted No-Effect Concentration (PNECs) for different environmental compartments by dividing dose descriptors with assessment factors.
| Compartment | Eco-toxicology Dose Descriptors | Assessment Factor | PNEC value |
|---|---|---|---|
| PNEC-Fresh water |
|
10 | 1mg/L |
| PNEC-STP microorganism | 3h-NOEC>1000mg/L (activated sludge inhibition test) | 10 | 100mg/L |
| PNEC-soil | LC50 (earthworm acute toxicity) >1000mg/kg | 1000 | 1mg/kg |
In above case, PNEC-water is calculated as 1mg/L. For aquatic environment, toxicological data (10mg/L) from the most sensitive species (Daphnia) is used for PNEC-water calculation. An assessment factor of 10 is used to take into account of the differences between laboratory conditions and natural conditions. If the actual concentration of the substance in aquatic environment is 2mg/L, the substance will cause unacceptable risks to aquatic enviroment.
How Many Predicted No-Effect Concentrations (PNECs) You Need to Derive?
PNECs need to be derived for various environmental compartments (water, sediment, soil, air, etc.). The table below summarizes the types of PNECs you may need to derive and how to calculate them.
| Compartment | PNEC | How to Get |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh Water | PNEC-fresh water |
|
| Marine Water | PNEC-marine water |
|
| Sediment | PNEC-sediment |
|
| Soil | PNEC-soil |
|
| Sewage treatment plant micro-organisms | PNEC-STP |
|
| Air | PNEC-air |
|
| Predator | PNEC-predator |
|
It is not always necessary to derive PNECs for all mentioned environmental compartments. Usually PNECs are only derived for 4 compartments: fresh water, soil, STP micro-organism and sediment.
How to Choose Appropriate Assessment Factors?
Assessment factors (AFs) are used to address the differences between laboratory data and natural conditions, taking into account of interspecies differences and intraspecies differences. Assessment factors applied for long-term tests are smaller because the uncertainty of the extrapolation from labs to natural environment is reduced. More data on more species in the same environmental compartment can also reduce uncertainties, thus further decreasing assessment factors.
The picture below summarizes common assessment factors used for PNEC calculation (from ECHA guidance on chemical risk assessment).
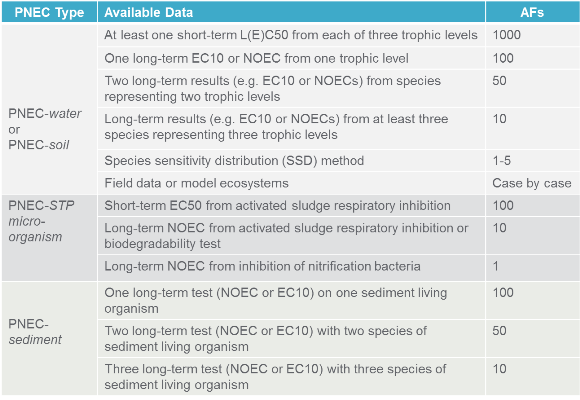
*Species representing 3 trophic levels : water (algae,fish and daphnia), soil (earthworm, plants, and micro-organisms).
Equilibrium Partitioning Method (EPM) for PNEC Calculation
In the absence of any ecotoxicological data for soil organisms or sediment-dwelling organisms, the PNEC-soil and PNEC-sediment may be provisionally calculated from PNEC-water using the equilibrium partitioning method (EPM). This method might result in overestimation or underestimation of toxicity and should only be considered as a screen for identifying substances requiring further testing on soil organisms and sediment-dwelling organisms .
Important: EPM is usually not recommended for substances that may pose a high hazard potential to soil organisms (i.e, logKow/Koc>5 and LC50/EC50 to <1mg/L to aquatic species).
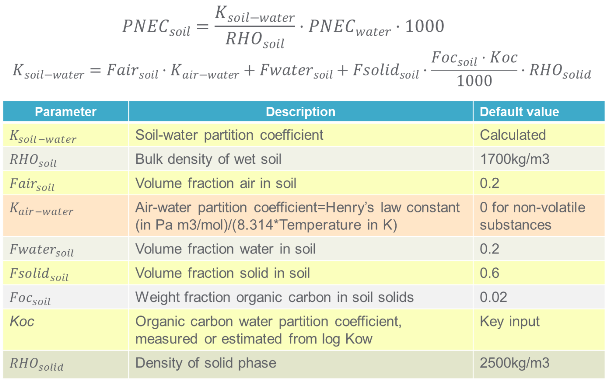
Calculating PNEC-soil from PNEC-water using EPM
The picture below shows you how to calculate PNEC-soil from PNEC-water using equilibrium partitioning method (EPM).
If default values were used, the above equations can be simplified to:
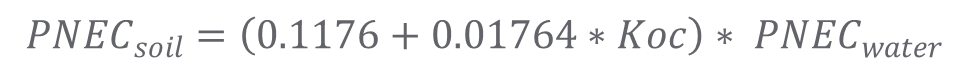
Note 1: Organic carbon-water partition coefficient Koc is a very important parameter for predicting PNEC-soil from PNEC-water. If Koc values are obtained from various types of soils, the mean value of Koc can be used for PNEC calculation. If you do not know what Koc is and how to get it, please click here.
Note 2: If only one test result with soil dwelling organisms is available, PNEC-soil is calculated on the basis of this result using assessment factors and on the basis of the equilibrium partition method (EPM). The lowest PNEC-soil value obtained will be used for risk assessment.
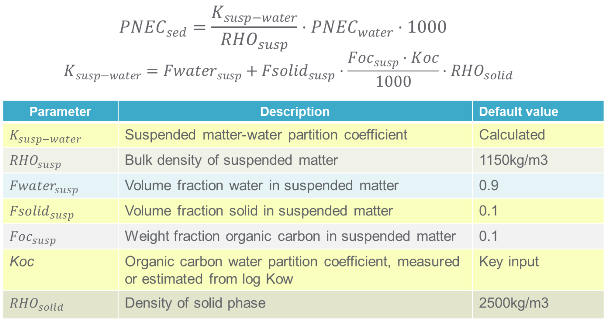
Calculating PNEC-sediment from PNEC-water using EPM
The picture below shows you how to calculate PNEC-sediment from PNEC-water using equilibrium partitioning method (EPM).
If default values were used, the above equations can be simplified to:
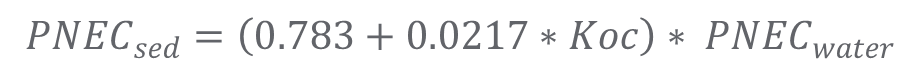
Note: For substances with a log Kow > 5 (or for compounds with a corresponding adsorption or binding behavior, e.g. ionisable substances, surface reactive substances), PNEC-soil and PNEC-sediment calculated need to be decreased by a factor of 10.
Quiz: Calculation of Predicted No-effect Concentration (PNEC)
You have been assigned with a task to derive PNECs for a substance (Koc=10) for 4 environmental compartments based on the available data below.
| Compartment | Available data | Method | PNEC |
|---|---|---|---|
| PNEC-Fresh water |
|
AF=? | ? |
| PNEC-STP microorganism | EC50(activated sludge inhibition test)=20mg/L | AF=? | ? |
| PNEC-soil | LC50 (earthworm acute toxicity) =500mg/kg | AF=? and EQM | ? |
| PNEC-sediment | No data | EQM | ? |
After calculating PNECs, please answer this question: if the concentration of the substance in water is 0.05mg/L, is this risk acceptable?
View quiz answer and explanation here.
Main Reference
- ECHA guidance on information requirements and chemical safety assessment Chapter R.10: Characterisation of dose [concentration]-response for environment
- ECHA guidance on information requirements and chemical safety assessment Chapter R.16: Environmental Exposure Estimation
- ECETOC: Soil and Sediment Risk Assessment of Organic Chemicals

Good job. You have learned what PNEC is, how many PNECs you need to derive, how to choose assessment factors and how to derive PNECs. We will cover how to estimate predicted environmental concentrations in a separate article. Please subscribe our newsletter to keep updated of our new articles.
"It does not matter how slowly you go as long as you do not stop. "
– Confucius
Having Questions?
We do not provide consultancy services. If you have questions or need any help, please contact our sponsor. You may also find an expert in CSP business directory below. If you are a consultant, you may get yourself listed in CSP business directory (free) or sponsor this page to leave your contact info on this page..

Tags: Topics - CRA, Environmental Risk Assessment