Introduction to Taiwan RoHS
Little Pro on 2016-09-21
15 Aug 2013, The Bureau of Standard, Metrology and Inspection (BSMI) published a voluntary national standard CNS 15663 Guidance to reduction of the restricted chemical substances in electrical and electronic equipment (EEE). CN15663 sets the scope of EEE products affected, the concentration limits of 6 hazardous substances and how to mark the presence of hazardous substances in EEE products. Since the standard is very similar to China RoHS regulation and EU RoHS regulation, it is often called Taiwan RoHS. In this article, we will talk about the scope of Taiwan RoHS, hazardous substance marking requirement and comparison with EU RoHS.
Scope of Taiwan RoHS
Taiwan RoHS applies to both large and small household appliances, IT and telecommunications equipment (including computers), consumer equipment, lighting equipment, electronic and electronic tools (except large scale stationary industrial tools), toys, leisure and sports equipment and automatic dispensers. National security or military use equipments, non-electrically driven equipments, fixed installation equipments and batteries are out of scope.
It shall be noted that CN15663 is a voluntary standard. Evaluation of CN15663 compliance is only mandatory for certain EEE products that are subject to mandatory inspection under the Commodity Inspection Act and announced by BMSI.
Taiwan RoHS Restricted Substances
Taiwan RoHS currently restricts the same 6 hazardous substances as EU RoHS 2 (except phthalates).
| Status | Substances and Limits |
|---|---|
| Current Restrictions |
|
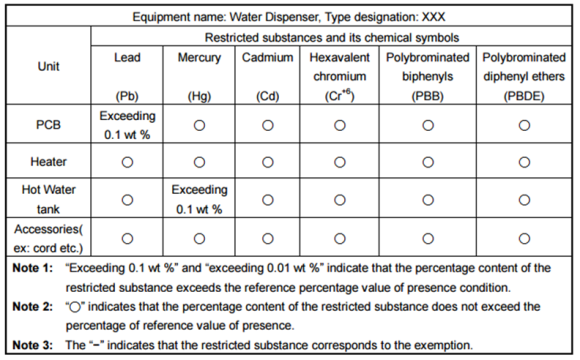
EEE products and their parts which contain certain hazardous substances exceeding above limits can still be sold in Taiwan provided that the presence of hazardous substances in affected products is marked. The names and content of the hazardous substances and affected components can be disclosed in a hazardous substance content table (see example below).
BMSI has also published two testing standards for above controlled substances: CNS 15050 Electro technical products-Determination of levels of six regulated substances (lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls, polybrominated diphenyl ethers) and CNS 15479 Method for determination of mercury level in fluorescent lamps.
Taiwan RoHS: Hazardous Substances Marking
The table below is an example of how to mark the presence of hazardous substances in EEE products by components. Companies shall clearly mark the hazardous substance content table on the body, packages, stickers, or the instruction books of the affected EEE products. Those who utilize website as a means to announce “the presence conditions of the restricted substances” shall clearly mark the website address on the body, packages, stickers, or the instruction books of the products.
Taiwan RoHS: Commodity Inspection Mark
For EEE products subject to mandatory inspection under the Commodity Inspection Act, BSMI could add RoHS compliance requirements to the mandatory conformity assessment scheme. Currently (as of 25 Aug 2016), the following products are subject to mandatory compliance with CN15663:
- From 1 Dec 2016 - drinking fountains;
- From 1 July 2017 – IT equipment, including automatic data processing machines, printers, photocopying machines, televisions and monitors. Also proposed for this date are projectors and lighting equipment, such as fluorescent tubes; and
- From 1 January 2018 – word processors, such as typewriters and cashiers (43 items in total) and wireless items, such as keyboards, mice and scanners (48 items in total).
- From 1 July 2018 - eight more items, including air conditioners and lighting
For products that have passed mandatory inspections, a modified BSMI Commodity Inspection Mark (see example below) needs to be put on the products in a prominent location. Basically it is an add-on to the current BSMI Commodity Inspection Mark to show the absence or presence of RoHS restricted substance in the product.
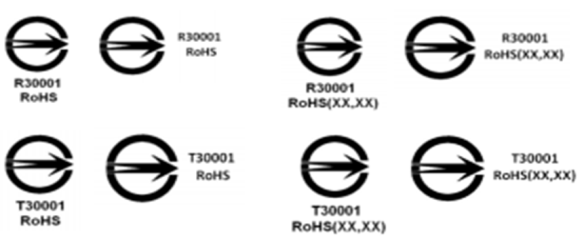
- Each mark bears a 5-digit identification number starting with R or T. The identification number and RoHS sign shall be placed to the below or right of the graphic symbol;
- RoHS means that all 6 hazardous substances do not exceed specified concentration limits;
- RoHS(XX,XX) means that the product contains certain hazardous substances that have exceeded specified concentration limits. For example, RoHS (Pb, Hg) indicates that the product contains Pb and Hg that have exceeded concentration limits.
Taiwan RoHS vs EU RoHS 2
| Items | Taiwan RoHS | EU RoHS 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Scope |
|
|
| Restricted Substances |
|
|
| Marking |
|
|
| Conformity Assessment |
|
|
References
- CNS15663 Guidance to reduction of the restricted chemical substances in electrical and electronic equipment
- ChemicalWatch: Taiwan issues voluntary RoHS guidelines
- ChemicalWatch: Taiwan adds more products to RoHS scope
- BMSI press release for adding more products to RoHS scope in Chinese
- Proposal for inspection requirements including marking of the presence conditions of the restricted substance on the legal inspection for 6 kinds of IT/AV products - English;
RoHS in Other Countries
| Country | Summary & Reference |
|---|---|
| China |
|
| Japan |
|
| Korea |
|
| Singapore |
|
| USA |
|
Having Questions?
We do not provide consultancy services. If you have questions or need any help, please contact our sponsor. You may also find an expert in CSP business directory below. If you are a consultant, you may get yourself listed in CSP business directory (free) or sponsor this page to leave your contact info on this page..
