GHS SDS Preparation Tip 1: How to Select Gloves for Chemicals
Little Pro on 2017-07-07
It requires significant knowledge and expertise to prepare a good and compliant SDS. Take section 8 exposure control and personal protection for example, you need to specify the appropriate type of gloves for worker to wear (material, thickness, min breakthrough time, etc). You cannot simply put "wearing gloves when handling" in section 8. This general statement does not provide enough value for worker protection since there is no single glove material able to provide unlimited resistance to any individual or combination of chemical agents. In this article, we will show you how to select gloves for chemicals in SDS section 8.
Regulatory Requirements
ECHA's guidance on SDS compilation has set detailed requirements on glove selection in section 8: "The type of gloves to be worn when handling the substance or mixture shall be clearly specified based on the hazard of the substance or mixture and potential for contact and with regard to the amount and duration of dermal exposure, including:– the type of material and its thickness, and – the typical or minimum breakthrough times of the glove material."
How to Choose Glove Material
UK HSE guide on protective gloves recommends the following suitable materials for different chemical groups (water soluble substances, organic solvents, strong acids, etc).
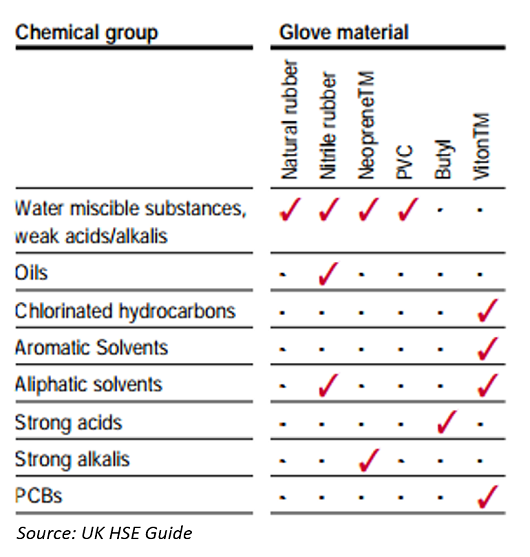
For strong acids or strong alkalis, only one glove material is suitable. For some chemical groups such as water soluble substances, multiple materials may be suitable. Where there is a choice of glove material, the extent of exposure to the chemical agent will be a significant factor in choosing between, for example, a neoprene glove or a less costly natural rubber.
How to Choose Thickness
The suitable thickness of a glove largely depends on the chemical resistance capability of glove material and the duration of exposure. Thicker gloves offer better protection but less flexibility. If the glove material is too thick or stiff, workers may decide not to wear them.
The thickness of typical gloves is usually expressed in mils or mm (4 mils = 0.1 mm). It ranges from 0.1 mm (4 mills) to 0.8 mm (32 mills). Here is a general guide for choosing appropriate thickness. Manufacturers of gloves shall always be consulted.
- 0.1 mm - 0.2 mm: usually disposable gloves, suitable for short exposure per use (usually less than 30 mins) or splash contact.
- 0.3 mm - 0.6 mm: good for regular industrial settings, suitable for medium exposure ( > 2 hours per day) or intermittent contact.
- > 0.6 mm: suitable for long exposure (>8 hours per day), full contact (i.e, total immersion), or heavy duty work .
How to Choose Breakthrough Time
Breakthrough time (BT) is defined as the elapsed time between initial contact of a liquid chemical with the outside surface of the glove and the time at which the permeation rate reaches 0.1 mg/m2/s. It depends on many factors such as:
- Thickness of glove material
- Concentration of the chemical worked with
- Amount of chemical the gloves come in contact with
- Length of time which the glove is exposed to the chemical
- Temperature at which the work is done
- Possibility of abrasion or puncture.
Most of glove suppliers test the breakthrough time of their gloves against various kinds of chemicals. Here is a general guide for choosing the breakthrough time of a glove. The minimum requirement is that the breakthrough time of a glove should be bigger than the duration of expected exposure.
- > 8 hours: excellent. If a worker needs to wear the same gloves all day (i.e, 8 hours per day), a breakthrough time bigger than 8 hours is usually recommended.
- 2-8 hours: good. Suitable for protecting workers from medium exposure and intermittent contact.
- 15 mins -2 hours: fair. Suitable for disposable gloves, short exposure per use or splash protection.
- <15 mins: not recommended for use. Manufactuers shall be consulted.
Practice: Choosing Right Glove for n-Hexane
Let's assume that you need to specify the suitable glove material, thickness and breakthrough time for n-hexane (belonging to Aliphatic solvents). You might need to give 2 options depending on potential contact and the duration of expected exposure.
| Scenarios | Suitable Gloves |
|---|---|
|
Full contact For example, cleaning metal parts by total immersion |
|
|
Splash contact For example, transfer of n-hexane from one container to the other. |
|
Note: Above numbers for thickness and breakthrough time are not fixed for n-Hexane. Other thickness or breakthrough time might also offer equal protection. When choosing gloves, please always seek expert help from the manufacturer/distributor of the chemical agent or glove. They are best placed to provide you with glove performance test data.
Reference
- ECHA guidance on the compilation of SDS
- Selecting gloves for work with chemicals - UK HSE
- Chemical Risistance Guide - Ansell
- Hand Protection Chemical Resistance Guide - VWR
Having Questions?
We do not provide consultancy services. If you have questions or need any help, please contact our sponsor. You may also find an expert in CSP business directory below. If you are a consultant, you may get yourself listed in CSP business directory (free) or sponsor this page to leave your contact info on this page..

Tags: Topics - GHS, GHS SDS and Labelling