UN Convention on Drug Precursor Chemicals
Little Pro on 2016-01-07
The United Nations Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances of 1988 entered into force on November 11, 1990. This Convention provides comprehensive measures against drug trafficking, including provisions against money laundering and the diversion of precursors chemicals.
In this article, we will focus on drug precursor chemicals. The table below gives you an overview of the Convention.
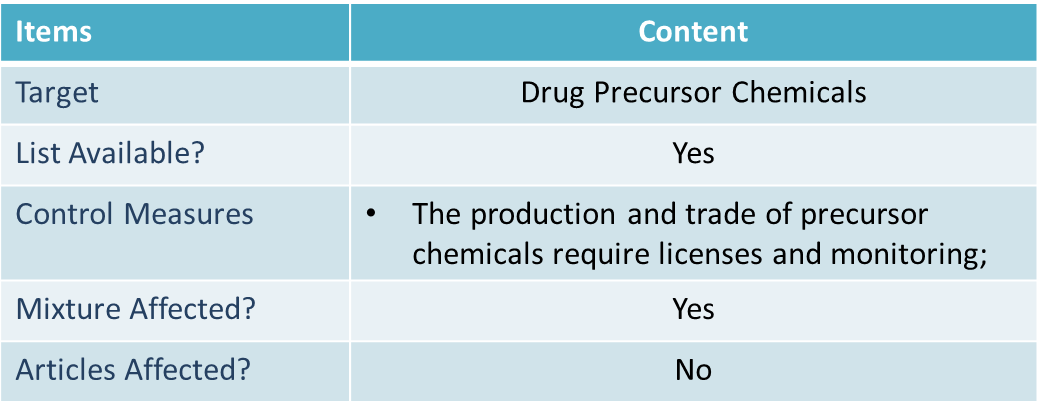
List of UN-Controlled Drug Precursors
Article 12 of the Convention establishes two categories of controlled illicit drug precursor substances, Table I and Table II. Generally Table I chemicals are more critical to the production of controlled substances than are those in the Table II, therefore provisions concerning these substances are more rigorous.
| Table 1 |
|
| Table 2 |
|
It shall be noted that:
- The salts of the substances listed in this Table are also regarded as listed whenever the existence of such salts is possible (except the salts of hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid);
- Mixtures containing listed substances may also be subject to control;
- Parties to the Convention usually have their own lists of controlled drug precursors. Such lists may contain more chemicals than those included in Table 1 and Table 2 (for example, China);
Impacts of the UN Convention on Drug Precursors Chemicals
The Convention requires that Parties take the measures to prevent diversion of substances listed in Table I and Table II and monitor the manufacture and distribution of substances in Table I and Table II.
Parties to the Convention have their own national regulations to control drug precursors (for example, China). Usually, the production, possession and import/export of listed chemicals require licenses. In addition to that, the manufacture and transaction of listed chemicals shall be documented and reported to national authorities (if required). Business operators need to check their own legislation for detailed requirements.
Reference & Resource
https://www.incb.org/incb/en/precursors/index.html
Having Questions?
We do not provide consultancy services. If you have questions or need any help, please contact our sponsor. You may also find an expert in CSP business directory below. If you are a consultant, you may get yourself listed in CSP business directory (free) or sponsor this page to leave your contact info on this page..

Tags: Topics - Convention, Controlled Chemicals Trade